AI use cases in Geotechnical Engineering

How can AI be used in Geotechnical Engineering?
Geotechnical engineering, a vital branch of civil engineering, delves into the complex behavior of earth materials and the design of structures, foundations, and slopes in contact with the ground. This field demands a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing soil mechanics, rock mechanics, geology, hydrology, and engineering geology. As such, geotechnical engineers must continuously adapt and innovate to address the challenges posed by the natural world.
In recent years, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous industries, and geotechnical engineering is no exception. The integration of AI into geotechnical practices offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance the understanding of earth materials and the performance of engineered structures. AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify intricate patterns, and make accurate predictions surpasses the capabilities of traditional methods.
At Civils.ai, we are a guiding light helping you to understand how this transformative technology can be used on your projects. If you have 15 minutes available feel free to watch our introductory video to AI in Geotechnical Engineering and if you want to learn more you can check out our full training course and suite of AI software we've developed.
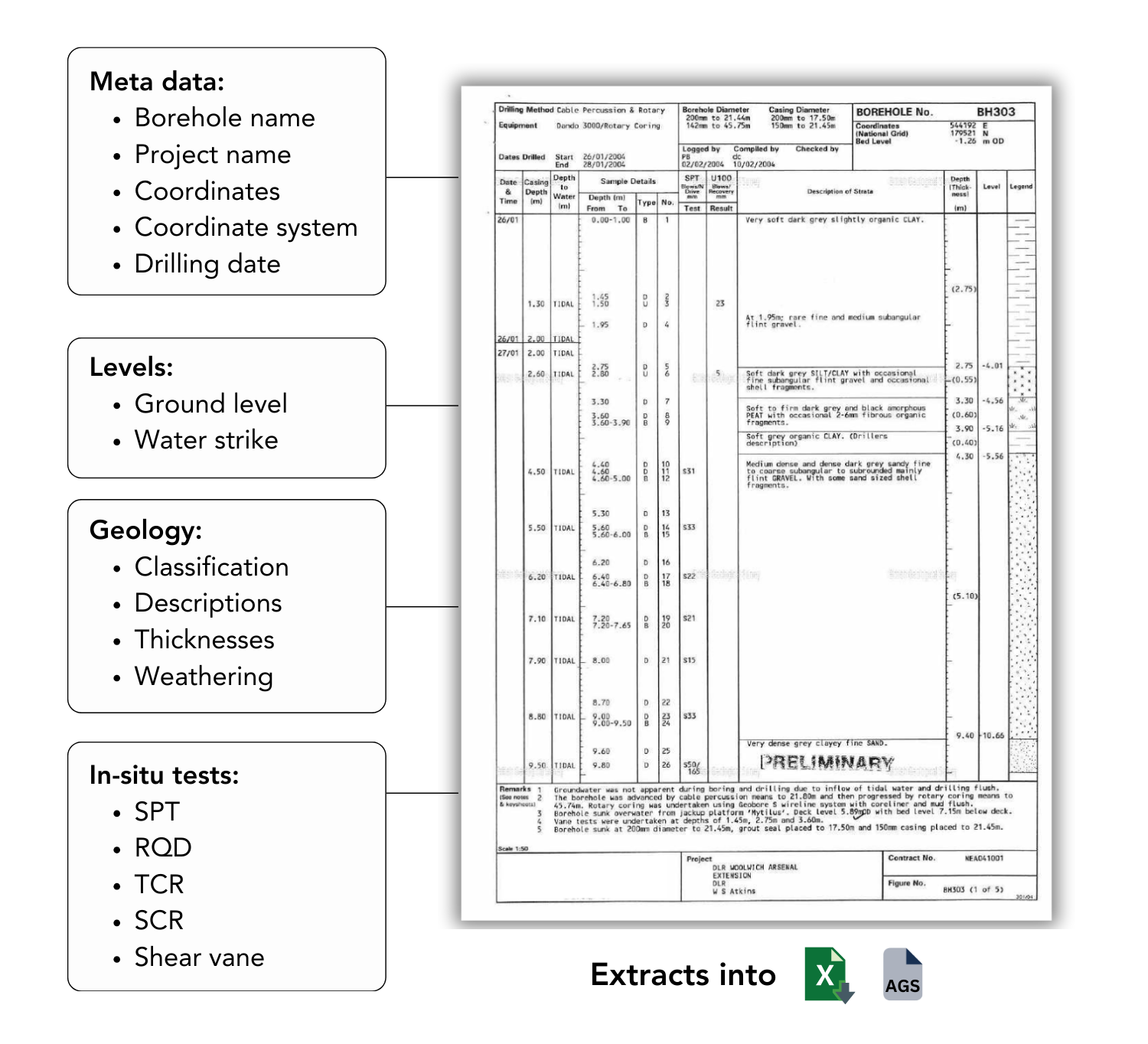
We developed various AI-powered tools since started our research 3 years ago. Our main tool is designed to automatically extract data from geotechnical reports and converting it into Excel, AGS, GIS and DXF file formats. Streamlining the process and reducing the risk of human error. Furthermore, our software can generate initial models of the subsurface, providing engineers with a more accurate and efficient starting point for their analyses. This innovative approach not only saves time but also significantly improves the reliability of geotechnical assessments.
As we delve into the practical applications of AI in geotechnical engineering, it becomes evident that this technology is not merely an enhancement but a necessity for future advancements in the field. Join us as we explore four practical examples of how AI is reshaping geotechnical engineering, making it more efficient, accurate, and insightful than ever before.
Practical Examples of AI in Geotechnical Engineering
In the dynamic field of geotechnical engineering, artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming traditional practices. By integrating AI technologies, geotechnical engineers, geologists, and professionals in geosciences can enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and data management capabilities. Here are four practical examples demonstrating how AI is revolutionizing geotechnical engineering.
1. Extracting Data from PDF Borehole Logs and Converting to Excel
One of the most time-consuming tasks in geotechnical engineering is extracting data from PDF borehole logs and converting it into a usable format such as Excel. AI-powered tools can automate this process, allowing engineers to quickly convert large volumes of borehole data into structured Excel files. These tools use optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP) to accurately read and interpret the data from scanned PDF documents, significantly reducing manual labor and the potential for human error. This streamlined data extraction process enables more efficient analysis and decision-making in geotechnical projects.
2. Automating Core Scans
Core samples are essential for understanding the geological composition of a site. Traditionally, analyzing these samples involves manual inspection and logging, which can be labor-intensive and subject to human error. AI-driven automation of core scans transforms this process by utilizing computer vision and machine learning algorithms to analyze core images. These AI systems can identify and classify different rock types, detect fractures, and measure core properties with high precision. Automating core scans not only accelerates the analysis but also provides more consistent and accurate results, enhancing the overall quality of geotechnical assessments.

3. Predictive Modeling for Soil Behavior
AI's capability in predictive modeling is a game-changer for geotechnical engineering. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, engineers can develop predictive models that simulate soil behavior under various conditions. These models are trained on historical geotechnical data and can forecast how soil will respond to different stressors, such as construction activities or natural disasters. Predictive modeling aids in risk assessment, helping engineers to design safer and more effective ground improvement strategies and to mitigate potential issues before they arise.
4. Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis of Geotechnical Data
The integration of AI with Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables real-time monitoring and analysis of geotechnical data. Sensors embedded in the ground can continuously collect data on parameters like soil moisture, pressure, and temperature. AI algorithms process this data in real-time, providing engineers with instant insights and alerts about any anomalies or potential issues. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, reducing the risk of geotechnical failures and ensuring the stability and safety of construction projects.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the immense potential benefits of AI in geotechnical engineering, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. One major hurdle is the availability and quality of data. Training AI algorithms requires large volumes of high-quality data, yet in many instances, such data is either unavailable or of poor quality. This lack of reliable data can limit the effectiveness and accuracy of AI models, potentially leading to less reliable outcomes.
Additionally, the time required to run AI models can be significant. Processing large datasets and running complex algorithms demand substantial computational resources and time, which can be a bottleneck in fast-paced project environments. The cost associated with running AI models is another consideration. High-performance computing infrastructure and cloud-based AI services can be expensive, adding to the overall project costs and potentially limiting accessibility for smaller firms or projects with limited budgets.
Accuracy limitations of current AI technologies also present a challenge. While AI can identify patterns and make predictions that surpass traditional methods, it is not infallible. The accuracy of AI models can be impacted by the quality of the training data, the complexity of the algorithms, and the inherent variability of geological conditions. These limitations necessitate cautious interpretation and validation of AI-generated results to ensure they are reliable and useful in practical applications.
The Future of AI in Geotechnical Engineering
Despite these challenges, the future of AI in geotechnical engineering is promising and exciting. As technology advances, the quality and availability of data are expected to improve, enhancing the effectiveness of AI models. Continued developments in computational power and cost-efficiency will make AI more accessible and practical for a broader range of applications and organizations.
Looking ahead, AI is poised to revolutionize geotechnical engineering. Enhanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring will enable engineers to design safer, more efficient, and more resilient structures. The collaboration between geotechnical engineers and AI researchers will be crucial in overcoming current limitations and unlocking the full potential of AI in the field.
By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in AI and actively exploring its applications, geotechnical engineers can harness the power of this transformative technology. The integration of AI into geotechnical practices will lead to innovative solutions, improved project outcomes, and a deeper understanding of earth materials and behaviors. The journey ahead is filled with opportunities for innovation and advancement, making it an exciting time for professionals in geotechnical engineering to embrace and shape the future of their field.